Climate TRACE Releases October 2025 Emissions Data
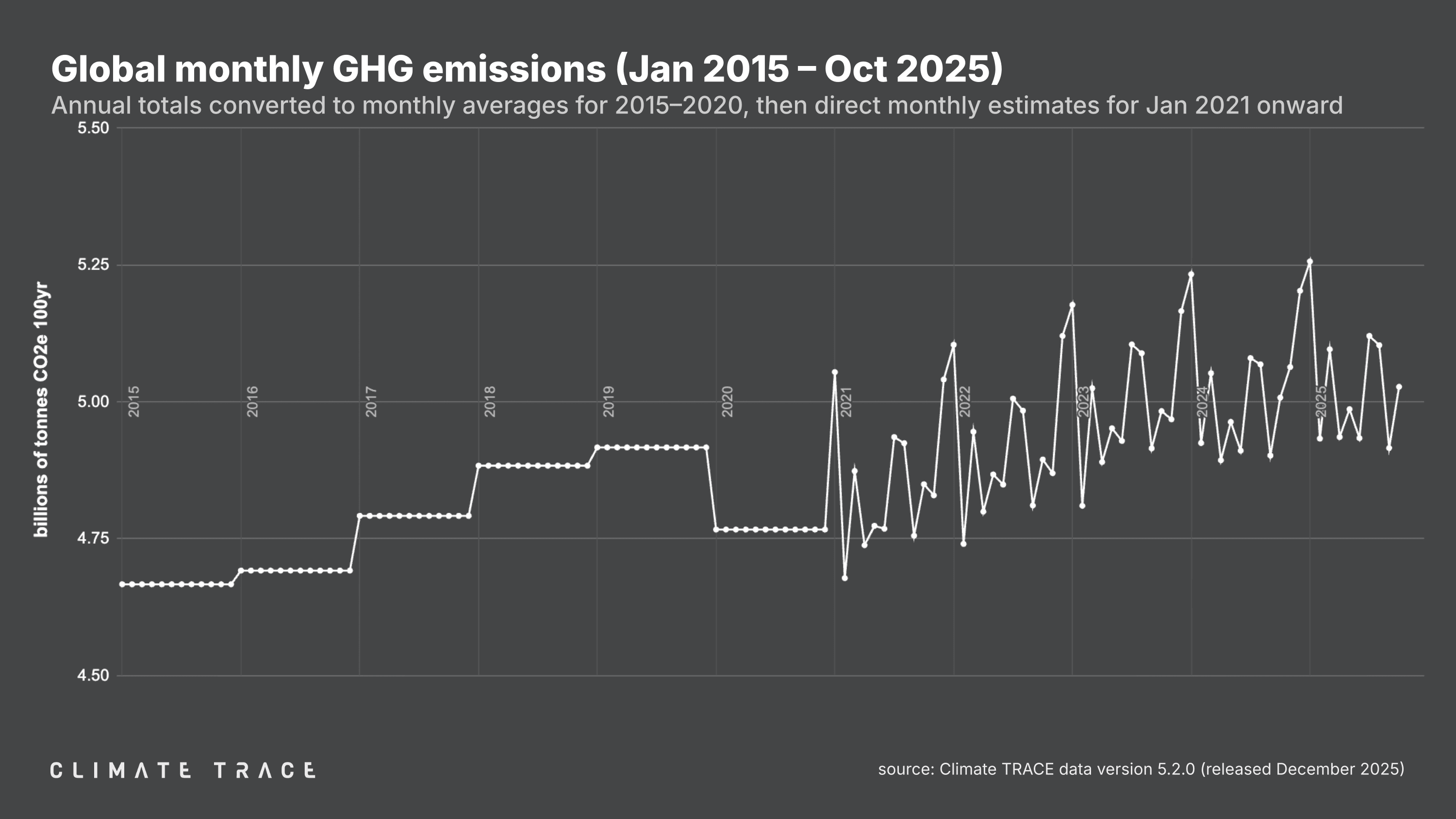
December 18, 2025 – Today, Climate TRACE reported that global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions for the month of October 2025 totaled 5.03 billion tonnes CO₂e. This represents an increase of 0.40% vs. October 2024. Total global year-to-date emissions are 50.31 billion tonnes CO₂e. This is 0.55% higher than 2024's year-to-date total. Global methane emissions in October 2025 were 33.83 million tonnes CH₄, an increase of 0.07% vs. October 2024.
Data tables summarizing GHG and primary particulate matter (PM2.5) emissions totals by sector and country, and GHG emissions for the top 100 urban areas for October 2025 are available for download here.
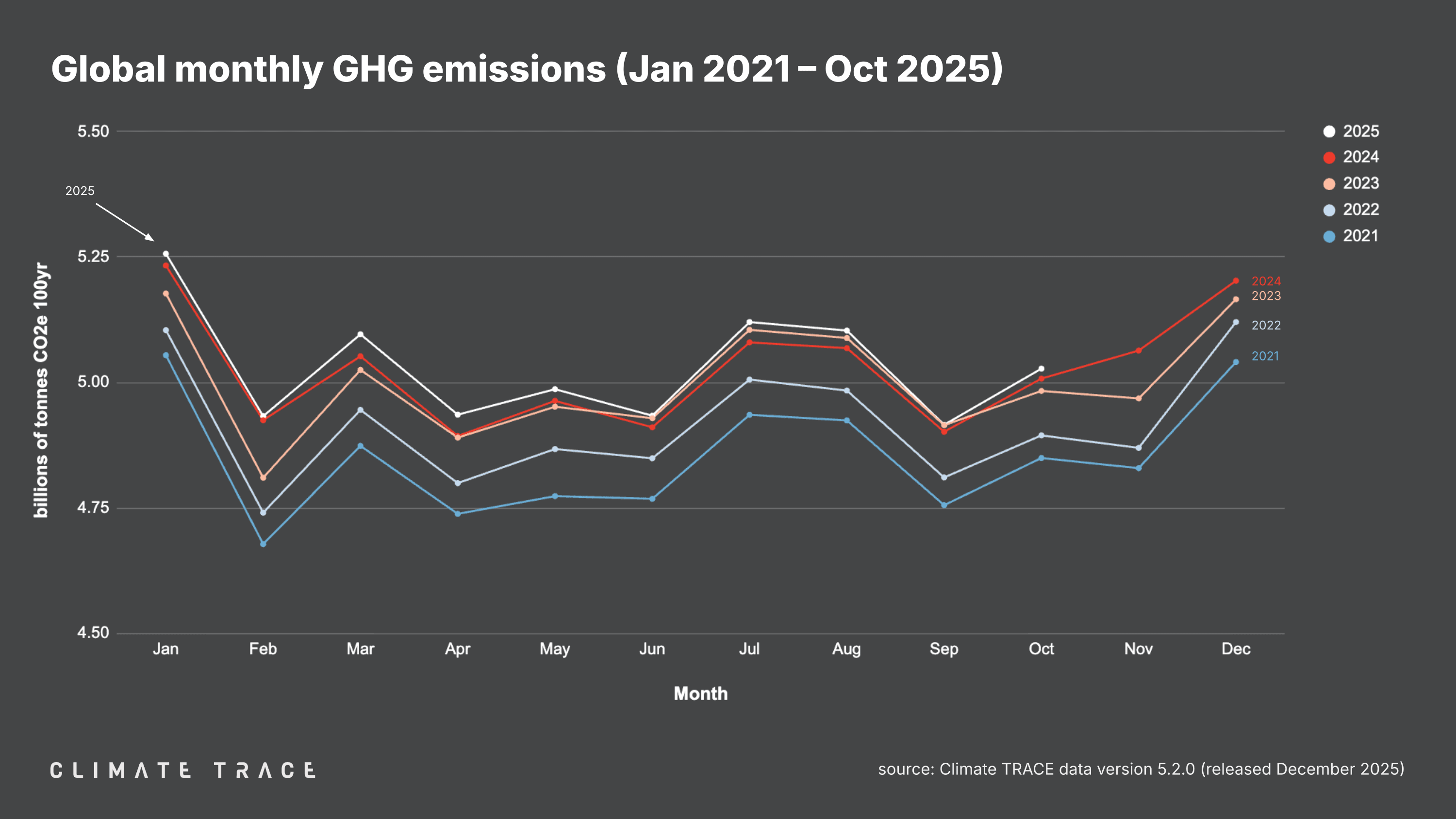
Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Country: October 2025
Climate TRACE's preliminary estimate of October 2025 emissions in China, the world's top emitting country, is 1.42 billion tonnes CO₂e, an increase of 8.46 million tonnes of CO₂e, or 0.60% vs. October 2024.
Of the other top five emitting countries:
-
United States emissions increased by 3.51 million tonnes CO₂e, or 0.61% year over year;
-
India emissions declined by 1.92 million tonnes CO₂e, or 0.53% year over year;
-
Russia emissions declined by 0.15 million tonnes CO₂e, or 0.05% year over year;
-
Indonesia emissions increased by 0.47 million tonnes CO₂e, or 0.37% year over year.
In the EU, which as a bloc would be the fourth largest source of emissions in October 2025, emissions declined by 1.43 million tonnes CO₂e compared to October 2024, or 0.46%.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Sector: October 2025
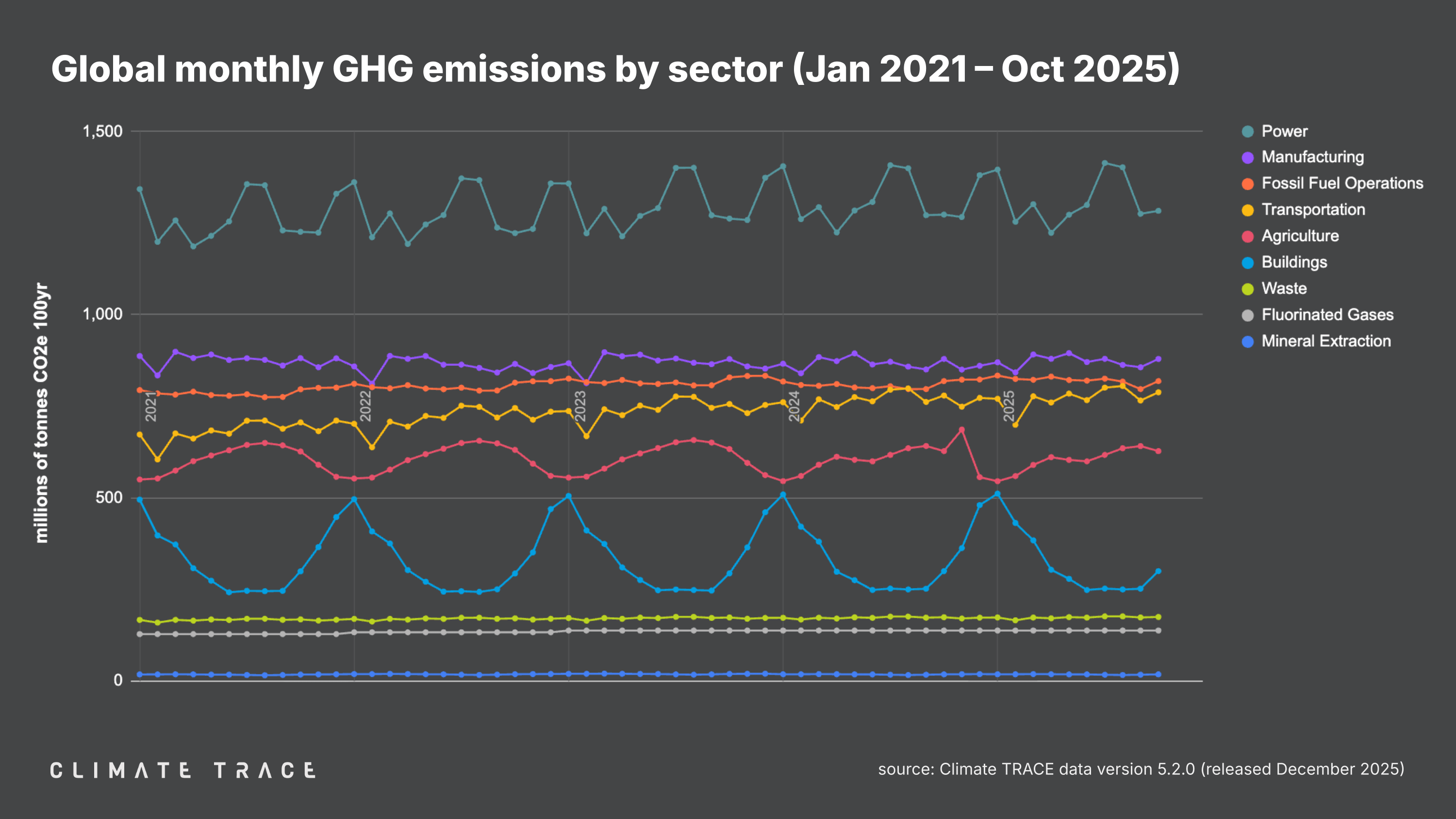
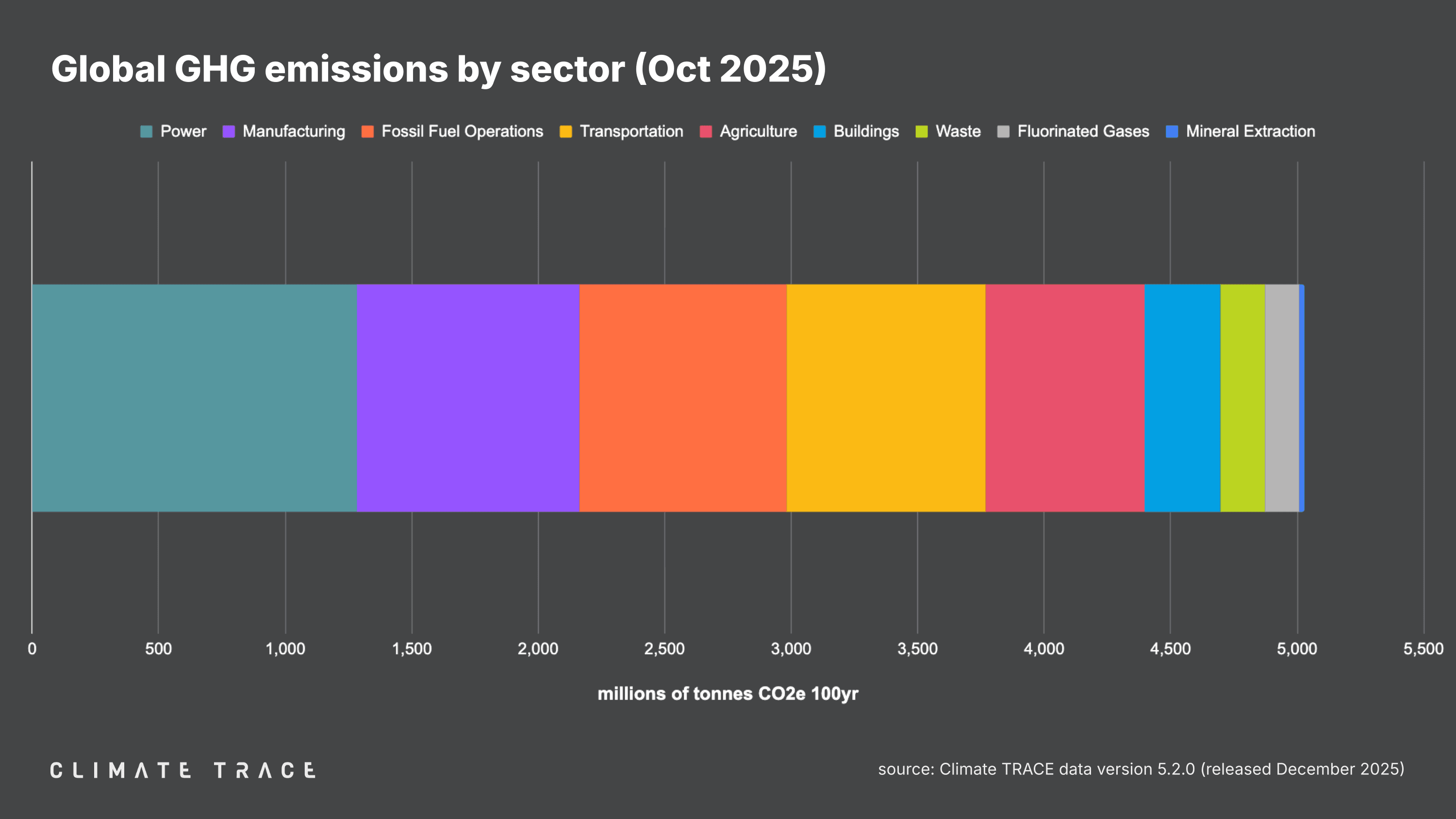
Greenhouse gas emissions increased in October 2025 vs. October 2024 in power, transportation, and waste, and did not decrease in any major sectors. Transportation saw the greatest change in emissions year over year, with emissions increasing by 1.13% as compared to October 2024.
-
Agriculture emissions were 627.58 million tonnes CO₂e, unchanged vs. October 2024;
-
Buildings emissions were 299.91 million tonnes CO₂e, unchanged vs. October 2024;
-
Fluorinated gases emissions were 137.71 million tonnes CO₂e, unchanged vs. October 2024;
-
Fossil fuel operations emissions were 818.64 million tonnes CO₂e, unchanged vs. October 2024;
-
Manufacturing emissions were 879.10 million tonnes CO₂e, unchanged vs. October 2024;
-
Mineral extraction emissions were 18.13 million tonnes CO₂e, unchanged vs. October 2024;
-
Power emissions were 1,283.56 million tonnes CO₂e, a 0.81% increase vs. October 2024;
-
Transportation emissions were 788.14 million tonnes CO₂e, a 1.13% increase vs. October 2024;
-
Waste emissions were 174.69 million tonnes CO₂e, a 0.35% increase vs. October 2024.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions by City: October 2025
The urban areas with the highest total GHG emissions in October 2025 were Shanghai, China; Tokyo, Japan; Houston, United States; New York, United States; and Los Angeles, United States.
The urban areas with the greatest increases in absolute emissions in October 2025 as compared to October 2024 were Ramagundam, India; Obra, India; Newcastle, Australia; Toranagallu, India; and Owensboro, United States. Those with the largest absolute emissions declines between this October and last October were Waidhan, India; Korba, India; Anpara, India; Rotterdam [The Hague], Netherlands; and UNNAMED, India.
The urban areas with the greatest increases in emissions as a percentage of their total emissions were Butibori, India; Uruguaiana, Brazil; Shitang, China; Obra, India; and Shostka, Ukraine. Those with the greatest decreases by percentage were Heilbronn, Germany; UNNAMED, India; Santaldih, India; Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, Russia; and Alotau, Papua New Guinea.
RELEASE NOTES
Revisions to existing Climate TRACE data are common and expected. They allow us to take the most up-to-date and accurate information into account. As new information becomes available, Climate TRACE will update its emissions totals (potentially including historical estimates) to reflect new data inputs, methodologies, and revisions.
With the addition of October 2025 data, the Climate TRACE database is now updated to version V5.2.0. This release expands asset coverage to include 245 additional power plants (globally) and 2,287 additional cattle operations (all in Japan). It includes non-greenhouse gas emissions for petrochemical steam cracking facilities in Asia Pacific and the Middle East. The waste sector has updated modeling for its landfill emissions: emissions are now modeled natively for each month, where previously, annual estimates were disaggregated into monthly estimates. The release also includes data fixes within transportation and waste sectors.
A detailed description of data updates is available in our changelog here.
To learn more about what is included in our monthly data releases and for frequently asked questions, click here.
All methodologies for Climate TRACE data estimates are available to view and download here.
For any further technical questions about data updates, please contact: coalition@ClimateTRACE.org.
To sign up for monthly updates from Climate TRACE, click here.
Emissions data for November 2025 are scheduled for release on January 29, 2026.
About Climate TRACE
The Climate TRACE coalition was formed by a group of AI specialists, data scientists, researchers, and nongovernmental organizations. Current members include Carbon Yield; Carnegie Mellon University's CREATE Lab; CTrees; Duke University's Nicholas Institute for Energy, Environment & Sustainability; Earth Genome; Former Vice President Al Gore; Global Energy Monitor; Global Fishing Watch/emLab; Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Lab; OceanMind; RMI; TransitionZero; and WattTime. Climate TRACE is also supported by more than 100 other contributing organizations and researchers, including key data and analysis contributors: Arboretica, Michigan State University, Ode Partners, Open Supply Hub, Saint Louis University's Remote Sensing Lab, and University of Malaysia Terengganu. For more information about the coalition and a list of contributors, click here.
Media Contacts
Fae Jencks and Nikki Arnone for Climate TRACE media@climatetrace.org


